
Traditional Meaning A modem (short for modulator–demodulator) is a device that converts signals so your computer or router can communicate with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Fiber Era: ONT Core Functions Types of Modems Modem vs Router vs Switch Device Role OSI Layer Example Modem Converts signals, connects to ISP Layer 1 (Physical) DSL/cable/fiber modem Router Connects different networks, directs packets Layer 3 (Network) Home router linking LAN to Internet Switch Connects devices within LAN, forwards by MAC Layer 2 (Data Link) Office switch connecting PCs & printers

What Is Domain Registration? Governance & Hierarchy Domain Name Space Reserved Domains Certain domains are reserved and cannot be registered:

IP Address Domain Name DNS (Domain Name System) Relationship Between Them Example: Summary

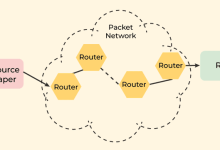
Routing Forwarding Relationship Example Summary

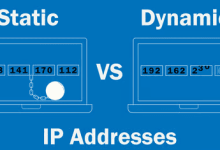
Static IP Dynamic IP Putting It Together Example Summary:

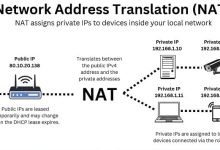
Public IP Address Private IP Address NAT (Network Address Translation) Putting It Together

IP Address MAC Address IP–MAC Binding Example Benefits Summary

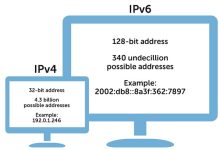
IP address allocation is the hierarchical infrastructure process of distributing unique numerical identifiers (IP addresses) to networks and devices, ensuring that data can be correctly routed across the global internet. IP Address Space Global Governance Who Gets the IPs Public IP Addresses Private IP Addresses Reserved IP Addresses Summary Table Category Routable on Internet Example Range / Address Purpose Quantity (approx.) Public IP Yes 8.8.8.8 Global communication ~3.7 billion usable (out of 4.3 billion total IPv4) Private IP No 192.168.0.0/16 Local networks (home/office) ~18 million addresses across 3 reserved ranges Reserved IP No (special use) 127.0.0.1, 169.254.0.0/16 Loopback, link-local, multicast ~600 million+ reserved for special functions “IPv4 has about 4.3 billion addresses (mostly exhausted), while IPv6 has ~3.4×10^38. IANA allocates blocks to RIRs,...

What Is a Service Provider? Internet Service Provider (ISP) Telecom Service Provider ⚙️ How They Work

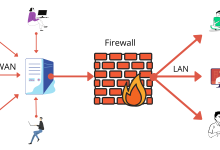
What Is a Firewall? Types of Firewalls How Firewalls Work

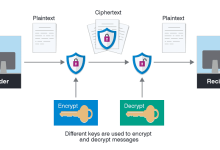
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts all your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, while a Proxy simply acts as an intermediary server that hides your IP address but does not encrypt your data. VPNs provide stronger privacy and security, whereas proxies are lighter and mainly used for location spoofing or bypassing restrictions. Proxy Server VPN vs Proxy Comparison Feature VPN Proxy Encryption Yes, full traffic encrypted No encryption IP Masking Yes Yes Scope Entire device traffic Specific apps/websites only Security High (protects against hackers/ISP) Low (traffic visible to ISP/hackers) Speed Slightly slower (due to encryption) Faster, but less secure Cost Usually paid Often free or cheaper

What Is a Computer Virus? Malware Common Types of Malwares Virus Common Types of Viruses What Is Antivirus? Types of Threats Antivirus Protects Against How Antivirus Works Relationship Between Virus and Antivirus











Latest Comments
666