
Terrestrial Fiber
What Is Terrestrial Fiber? Structure & Technology Types of Terrestrial Fiber Networks Global Scale

What Is Terrestrial Fiber? Structure & Technology Types of Terrestrial Fiber Networks Global Scale

How Satellite Links Work Types of Satellite Links Applications Comparison with Other Infrastructure Feature Submarine Cables Terrestrial Fiber Satellite Links Coverage Intercontinental National/regional Global, including remote areas Latency Very low Very low Higher (depends on orbit) Capacity Extremely high Extremely high Lower than fiber/cables Reliability High High Weather/space conditions affect Deployment Undersea cable ships Underground/land routes Launch satellites into orbit

Hosting refers to providing space and resources on servers so that websites, applications, or services can be accessible over the internet.It allows individuals and organizations to publish content online without needing to own and manage their own physical servers. Types of Hosting 1. Shared Hosting 2. VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server) 3. Dedicated Hosting 4. Cloud Hosting 5. Managed Hosting
Cloud computing is the on‑demand delivery of computing resources over the internet. These resources include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics. Instead of owning hardware, organizations and individuals rent resources from cloud providers, paying only for what they use. Core Principles Deployment Models Cloud Computing Products & Services 1.Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) 2. Platform as a Service (PaaS) 3. Software as a Service (SaaS) 4. Container as a Service (CaaS) 5. Function as a Service (FaaS / Serverless)
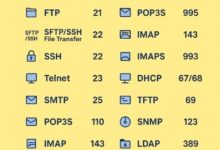
What Are Protocols? What Are Ports? Common Protocols & Ports Protocol Port Transport Use HTTP 80 TCP Web traffic (unencrypted) HTTPS 443 TCP Secure web traffic FTP 21 TCP File transfer SMTP 25 TCP Sending email DNS 53 UDP/TCP Domain name resolution SSH 22 TCP Secure remote login Telnet 23 TCP Remote login (insecure, legacy) SNMP 161 UDP Network management NTP 123 UDP Time synchronization How Protocols & Ports Work Together Security Considerations Summary:
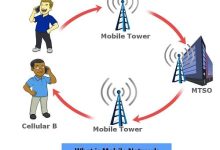
A mobile network is a type of wireless network that enables devices to communicate without fixed cables. It relies on: Generations of Mobile Networks Generation Year Technology Speed Key Features 1G 1980s Analog ~2.4 kbps Voice only, poor security 2G 1990s Digital (GSM, CDMA) ~64 kbps SMS, MMS, better voice quality 3G 2000s UMTS, WCDMA ~2 Mbps Mobile internet, video calls 4G 2010s LTE ~100 Mbps HD streaming, mobile broadband 5G 2020s NR (New Radio) ~10 Gbps Ultra-low latency, IoT, AR/VR Key Characteristics Applications
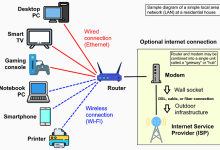
Local Area Network (LAN) A LAN (Local Area Network) is a computer network that connects devices within a limited physical area — such as a home, office, or school. It allows devices to share resources (files, printers, internet) and communicate at high speed. Key Characteristics Relationship with Wi‑Fi LAN vs WAN Feature LAN WAN Coverage Local area (home, office, campus) Wide area (cities, countries) Speed High (100 Mbps–10 Gbps) Lower, depends on telecom infra Ownership Private, managed locally Shared/public infrastructure Connection Ethernet, Wi‑Fi Fiber, satellite, leased lines
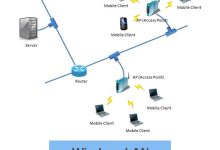
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) A WLAN is a type of LAN (Local Area Network) that uses wireless communication (radio waves) instead of physical cables to connect devices. The most common WLAN technology is Wi‑Fi (IEEE 802.11 standard). Key Characteristics Wi‑Fi: Standards, Versions, and History 1. Origins 2. Generations of Wi‑Fi Generation Standard Year Band Max Speed Key Features Wi‑Fi 1 802.11 1997 2.4 GHz 2 Mbps First Wi‑Fi standard Wi‑Fi 2 802.11b 1999 2.4 GHz 11 Mbps Affordable, but interference-prone Wi‑Fi 3 802.11g 2003 2.4 GHz 54 Mbps Faster, backward compatible Wi‑Fi 4 802.11n 2009 2.4 & 5 GHz 600 Mbps Introduced MIMO, dual-band Wi‑Fi 5 802.11ac 2014 5 GHz 1.3 Gbps Beamforming, better streaming Wi‑Fi 6 802.11ax 2019 2.4 & 5 GHz 9.6 Gbps OFDMA,...
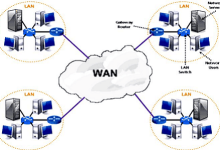
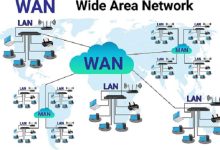
Wide Area Network (WAN) A WAN is a computer network that spans a large geographic area — from cities to entire countries or globally. It connects multiple LANs (Local Area Networks) together, enabling communication and resource sharing across long distances. The Internet itself is the largest WAN. Key Characteristics Examples 4. Challenges WAN vs Internet WAN vs LAN vs WLAN Feature LAN WLAN WAN Coverage Local (home, office, campus) Local, wireless (Wi‑Fi) Wide area (cities, countries) Connection Ethernet cables Wi‑Fi radio waves Telecom lines, satellites, fiber Speed Very high (100 Mbps–10 Gbps) Variable (depends on Wi‑Fi standard) Lower, depends on distance/infra Ownership Private Private Mix of private & public
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a computer network that covers a city or metropolitan area. It is larger than a LAN (Local Area Network) but smaller than a WAN (Wide Area Network). MANs connect multiple LANs across a city, often using high‑speed fiber optic cables. Key Characteristics Examples LAN vs MAN vs WAN Feature LAN MAN WAN Coverage Building, campus City or metropolitan area Country, continent, global Speed Very high (100 Mbps–10 Gbps) High (hundreds Mbps–Gbps) Lower, depends on distance/infra Ownership Private (home, office) Telecoms, governments, universities Mix of private & public Example Home Wi‑Fi, office LAN Citywide university network The Internet, global corporate WAN
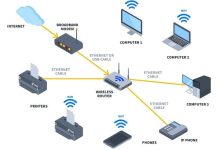
A router is a device that sits at the boundary between networks and decides where to send data packets. It connects multiple IP networks or subnetworks and ensures that traffic flows efficiently. Core Functions Types of Routers Router vs Switch vs Modem Device Role Layer Example Router Connects different networks, directs packets Layer 3 (Network) Home router linking LAN to Internet Switch Connects devices within one LAN Layer 2 (Data Link) Office switch connecting PCs & printers Modem Converts signals for ISP connection Layer 1 (Physical) DSL/cable modem providing Internet
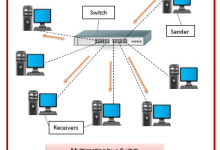
A switch is a networking device that connects multiple devices (computers, printers, servers) within the same Local Area Network (LAN) and forwards data intelligently based on MAC addresses. How It Works Types of Switches Key Functions Switch vs Router vs Hub Device Role Layer Example Switch Connects devices within a LAN, forwards by MAC Layer 2 Office PCs connected together Router Connects different networks, forwards by IP Layer 3 Home LAN to Internet
Latest Comments
666