
According to a report released by data agency IDC, OPPO became the only leading smartphone brand in China to achieve growth against the market trend in the third quarter. In the first three quarters of this year, the Reno series helped OPPO secure the top position in shipments within the highly competitive $400–600 price segment. With its trendy design and innovative imaging capabilities, the OPPO Reno series has reached nearly 100 million activations in the Chinese market. During the summer months of June and July, when students purchase phones in large numbers, the Reno14 ranked as the best‑selling Android single model across all price ranges. Information shows that the Reno14 series was officially released in May this year, with a...

Data shows that after its launch in Spain, OPPO Find X9 sales in just two weeks reached nearly five times that of its predecessor, while the overall overseas sales of the Find X9 series have already doubled compared to the previous generation. OPPO Find series product manager Zhou Yibao also revealed that the Find X9 series is not only popular in Europe but has achieved success globally. In addition, the high‑end Find X9 Pro version has recorded overseas sales almost three times higher than its predecessor. The Find X9 series consists of two models: Find X9 and Find X9 Pro. The Find X9 features a 6.59‑inch 1.5K flat display, powered by the MediaTek Dimensity 9500 platform. It houses a 7025mAh...

OPPO A6l officially went on sale, offered in a single 12GB+256GB version. The OPPO A6l is powered by the Snapdragon 7 Gen 3 chipset built on a 4nm process, achieving an AnTuTu benchmark score of over 890,000. It supports up to 12GB memory expansion, combined with Aurora Engine + Tide Engine, promising smooth performance for up to six years. The device also features OPPO’s self‑developed “Shanhai” communication enhancement chip, with a full‑surround antenna layout in the middle frame. Signal strength in weak networks is boosted by 200%, and it supports communication without a network. It comes with dual‑band GPS and tri‑band BeiDou positioning. Inside is a 7,000mAh long‑life battery designed to last six years. On a full charge, it supports...

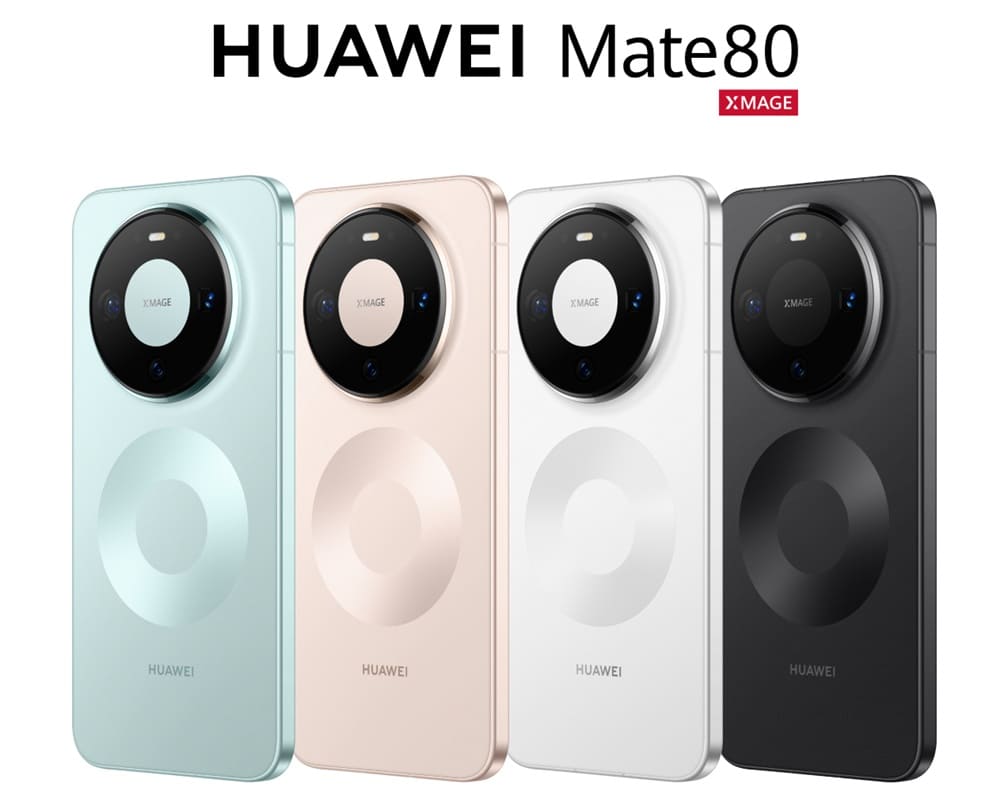
The Samsung Galaxy Z TriFold and Huawei Mate XT series take completely different approaches. Samsung adopts a dual‑screen “G‑shaped” folding design, where the flexible large display is protected inside when folded, naturally offering more protection than Huawei’s solution and giving it a significant advantage in drop resistance. Of course, this design has pros and cons—the biggest drawback is the higher weight and thickness. You immediately feel the heft when holding it, since it uses dual hinges and dual screens. The device weighs 309g, close to a can of soda, and measures 12mm thick when fully folded. At the same time, you can sense Samsung’s consistent premium feel in foldables: the craftsmanship is meticulous, the edges don’t feel sharp in the...

A blogger has created a rendering of the Xiaomi 17 Ultra’s appearance, and the device will be officially released this month. Compared with the Xiaomi 17 Pro Max, the biggest change in the Xiaomi 17 Ultra is the adoption of a circular camera module without a rear display, while the overall design remains consistent with the previous generation. In detail, the Xiaomi 17 Ultra features a Leica triple-camera setup on the back: a 200‑megapixel periscope telephoto lens at the top, with a 1‑inch main camera and an ultra‑wide‑angle lens below. On the front, it has a flat display, expected to use the same “Super Pixel New National Screen” as the Xiaomi 17 Pro Max. Each pixel contains independent red, green,...


Basic Definition Technology Coverage & Capacity Pros & Cons Types

DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) Cable Internet Fiber Internet Satellite Internet Mobile Broadband (4G/5G) Type Technology Speed Range Pros Cons Best For DSL Telephone lines 1–100 Mbps / 1–10 Mbps Widely available, cheap Slow, distance-sensitive Rural/suburban Cable Coaxial cables 50 Mbps–1 Gbps / 5–50 Mbps Faster than DSL, common Shared bandwidth, weak upload Urban households Fiber Fiber-optic cables 1–10 Gbps+ (symmetrical) Fastest, reliable, low latency Expensive, limited coverage Heavy users/business Satellite Satellites 25–250 Mbps / 5–20 Mbps Works anywhere High latency, weather issues Remote areas Mobile Cellular (4G/5G) 10 Mbps–1 Gbps+ Portable, flexible Coverage/data caps On-the-go users

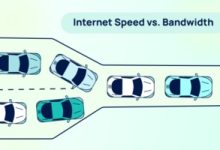
Bandwidth Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given time. Usually measured in bits per second (bps), such as Mbps (megabits per second) or Gbps (gigabits per second). Key Points Speed Speed in networking refers to how quickly data travels from one point to another. It is the rate of data transfer experienced by the user, often measured in bits per second (bps), just like bandwidth. Key Points Bandwidth vs Speed vs Throughput Term Definition Example Key Point Bandwidth Maximum capacity of a network link, measured in bits per second (bps). A fiber line with 1 Gbps bandwidth Think of it as the width of the highway (how many cars...

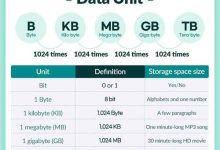
What is a Data Unit? A data unit is the basic piece of information used in computing and networking. Depending on the context, it can mean: Storage / Capacity Data Units These measure the size of data in computers and digital systems: Used to describe file sizes, disk capacity, memory, and bandwidth. Networking Transmission Data Units (OSI Model) These describe how data is packaged and transmitted across networks: Each layer adds headers/trailers to guide transmission and ensure reliable communication. Bandwidth and Data Units Final Summary

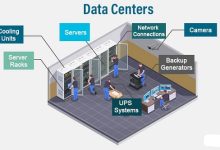
What Is a Data Center? Key Components Types of Data Centers Global Scale Why They Matter

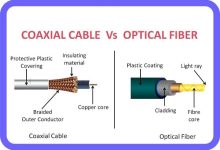
What Are Submarine Cables? History Structure of Modern Submarine Cables A typical cross‑section includes: Deployment Global Scale















Latest Comments
666