IP Address Allocation
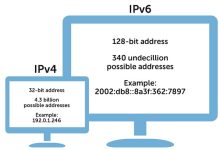
IP address allocation is the hierarchical infrastructure process of distributing unique numerical identifiers (IP addresses) to networks and devices, ensuring that data can be correctly routed across the global internet. IP Address Space Global Governance Who Gets the IPs Public IP Addresses Private IP Addresses Reserved IP Addresses Summary Table Category Routable on Internet Example Range / Address Purpose Quantity (approx.) Public IP Yes 8.8.8.8 Global communication ~3.7 billion usable (out of 4.3 billion total IPv4) Private IP No 192.168.0.0/16 Local networks (home/office) ~18 million addresses across 3 reserved ranges Reserved IP No (special use) 127.0.0.1, 169.254.0.0/16 Loopback, link-local, multicast ~600 million+ reserved for special functions “IPv4 has about 4.3 billion addresses (mostly exhausted), while IPv6 has ~3.4×10^38. IANA allocates blocks to RIRs,...