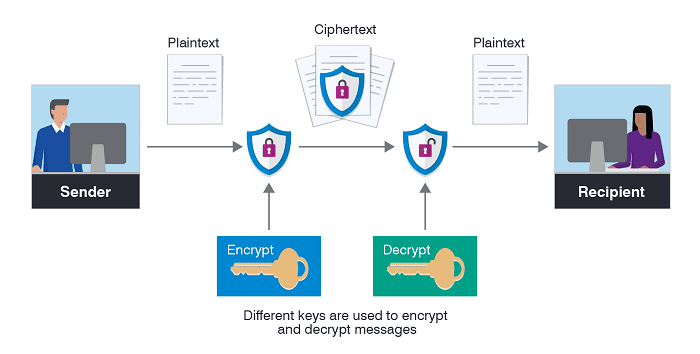
🔑 What Is Encryption?
- Definition: Encryption is the process of converting readable information (plaintext) into unreadable format (ciphertext) using algorithms and keys.
- Purpose: Protects confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data.
- How it works:
- Sender uses an encryption algorithm and a key to transform plaintext into ciphertext.
- Ciphertext is transmitted or stored.
- Recipient uses a decryption key to convert ciphertext back into plaintext.
🧩 Types of Encryptions
- Symmetric Encryption: Same key for encryption and decryption (e.g., AES).
- Asymmetric Encryption: Public key for encryption, private key for decryption (e.g., RSA, ECC).
- Hashing (related but different): One‑way transformation, used for integrity checks (e.g., SHA‑256).
🔐 Password Encryption (Process)
When we talk about passwords, encryption or hashing is critical for security. Here’s the step‑by‑step process:
- Input plaintext password
- User types
"MyPassword123"into a login form.
- User types
- Algorithm selection
- System chooses an algorithm:
- Symmetric (AES) or asymmetric (RSA) for transmission.
- Hashing (SHA‑256, bcrypt, PBKDF2) for storage.
- System chooses an algorithm:
- Key or salt generation
- Encryption uses keys.
- Hashing often adds a salt (random string) to strengthen security.
- Transformation
- Plaintext → Ciphertext or Hash.
- Example:
"MyPassword123"→a5f3c6a11b...(SHA‑256 hash).
- Storage/Transmission
- Stored in database as hash (not plaintext).
- Transmitted over network with encryption (TLS/SSL).
- Verification
- User enters password again.
- System applies the same algorithm.
- Compares result with stored hash/ciphertext.
- If match → access granted.
⚙️ Where Encryption Is Used
- Data at rest: Files, databases, storage devices.
- Data in transit: HTTPS, VPNs, messaging apps.
- Authentication: Passwords, digital signatures, certificates.
- Cloud security: Protects sensitive data stored remotely.
📌 Benefits
- Confidentiality → prevents unauthorized access.
- Integrity → ensures data hasn’t been altered.
- Authentication → confirms identity.
- Compliance → meets legal/regulatory requirements.




Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up