🔌 Network Switch
1. Definition
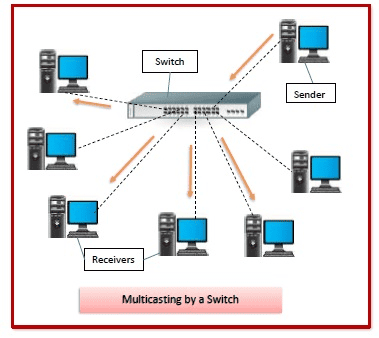
A switch is a networking device that connects multiple devices (computers, printers, servers) within the same Local Area Network (LAN) and forwards data intelligently based on MAC addresses.
2. How It Works
- Operates at Layer 2 (Data Link) of the OSI model.
- Each port on the switch learns the MAC address of the device connected to it.
- When a packet arrives, the switch looks up the destination MAC in its MAC address table and forwards the packet only to the correct port.
- This makes communication faster and reduces unnecessary traffic compared to older hubs (which broadcast to all ports).
3. Types of Switches
- Unmanaged switch:
- Plug‑and‑play, no configuration needed.
- Common in small home/office setups.
- Managed switch:
- Configurable (VLANs, QoS, monitoring).
- Used in enterprise networks.
- Layer 3 switch:
- Combines switching (Layer 2) with routing (Layer 3).
- Can make IP‑based forwarding decisions like a router.
4. Key Functions
- MAC learning: Builds a table of MAC addresses and ports.
- Forwarding/filtering: Sends packets only to the correct destination port.
- Broadcast control: Limits unnecessary traffic.
- VLAN support (in managed switches): Segments a LAN into smaller logical networks.
5. Example in Action
- In an office:
- 20 PCs, 2 printers, and a server are all connected to a switch.
- The switch ensures that when PC1 sends data to the server, only the server’s port receives it — not all 20 PCs.
6. Switch vs Router vs Hub
| Device | Role | Layer | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Switch | Connects devices within a LAN, forwards by MAC | Layer 2 | Office PCs connected together |
| Router | Connects different networks, forwards by IP | Layer 3 | Home LAN to Internet |
| Hub | Broadcasts to all devices (no intelligence) | Layer 1 | Legacy networks, rarely used today |
✅ Summary: A switch is the “traffic manager” inside a LAN. It connects devices and forwards data only where it needs to go, using MAC addresses. Modern networks rely on switches for efficiency, scalability, and security.




Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up