🌐 IP, Domain, and DNS
1. IP Address
- Definition: An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical identifier for a device on a network.
- Types:
- IPv4: 32‑bit, written as four numbers (e.g.,
192.168.1.1). - IPv6: 128‑bit, written in hexadecimal (e.g.,
2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334).
- IPv4: 32‑bit, written as four numbers (e.g.,
- Role: Machines use IP addresses to locate and communicate with each other.
- Problem: Numbers are hard for humans to remember.
2. Domain Name
- Definition: A domain name is a human‑friendly label that maps to an IP address.
- Examples:
google.com→ maps to an IP like142.250.190.14.microsoft.com→ maps to an IP like20.81.111.85.
- Structure:
- Top‑Level Domain (TLD):
.com,.org,.net,.cn, etc. - Second‑Level Domain:
google,microsoft. - Subdomain:
mail.google.com,docs.microsoft.com.
- Top‑Level Domain (TLD):
- Role: Makes the Internet easier to use by replacing numbers with names.
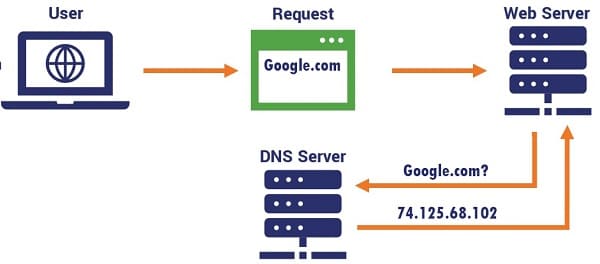
3. DNS (Domain Name System)
- Definition: DNS is the “phonebook of the Internet”, translating domain names into IP addresses.
- How it works:
- You type
www.example.comin your browser. - Your computer asks a DNS resolver for the IP.
- The resolver queries DNS servers (root → TLD → authoritative).
- The IP address is returned (e.g.,
93.184.216.34). - Your browser connects to that IP.
- You type
- Key Components:
- Root servers: Handle top‑level domains.
- TLD servers: Handle
.com,.org, etc. - Authoritative servers: Store actual domain‑to‑IP mappings.
- Caching: DNS results are cached locally and by ISPs to speed up lookups.
4. Relationship Between Them
- IP: The actual numeric address of a device.
- Domain: A human‑readable name pointing to that IP.
- DNS: The system that translates between the two.
👉 Example:
- You type
www.microsoft.com. - DNS finds its IP (e.g.,
20.81.111.85). - Your browser connects to that IP, and the website loads.
✅ Summary
- IP = numeric identifier.
- Domain = human‑friendly name.
- DNS = translator between domain and IP. Together, they make the Internet usable for both machines and humans.




Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up