📡 Routing vs Forwarding
1. Routing
- Definition: The decision-making process of determining the best path for data packets to travel across a network.
- Who does it: Routers (using routing tables and protocols).
- Key points:
- Involves building and maintaining a routing table.
- Uses routing protocols (e.g., RIP, OSPF, BGP) to exchange information with other routers.
- Considers metrics like hop count, bandwidth, latency, and policy.
- Analogy: Like planning a road trip — choosing which highways and roads to take before you start driving.
2. Forwarding
- Definition: The actual act of sending a packet from one interface to another, based on the routing table’s decision.
- Who does it: Routers and switches.
- Key points:
- Uses the forwarding table (derived from the routing table).
- Happens at high speed, often in hardware (ASICs).
- Focuses only on moving the packet to the next hop.
- Analogy: Like driving along the chosen road — once the route is decided, forwarding is just following it.
3. Relationship
- Routing = thinking (deciding the path).
- Forwarding = doing (sending the packet along that path).
- Routing is control‑plane logic; forwarding is data‑plane action.
4. Example
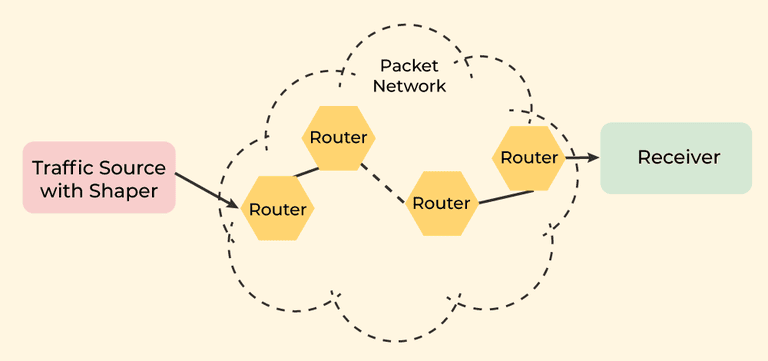
- You send a message from your laptop in Manila to a server in New York.
- Routing: Routers decide the best path across the Internet (via Hong Kong → Los Angeles → New York).
- Forwarding: Each router along the way physically passes the packet to the next router according to the chosen path.
✅ Summary
- Routing = decision process (control plane).
- Forwarding = packet delivery (data plane). Together, they ensure data travels efficiently across networks
Article Title:《What is Routing and Forwarding》
Article Link:
https://sslgadgets.com/internet/networking/ip-addressing/what-is-routing-and-forwarding/
Images and content in this article are sourced from the internet. If any copyright infringement is found, please contact us for removal.




Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up