🌐 Public vs Private IP & NAT
1. Public IP Address
- Definition: An IP address assigned by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) that is visible on the Internet.
- Scope: Globally unique, registered with organizations like InterNIC.
- Use case: Websites, servers, or any device that must be directly accessible online.
- Example ranges: Any IP not reserved for private use (e.g., 8.8.8.8 for Google DNS).
- Pros: Enables direct communication across the Internet.
- Cons: Less secure, consumes limited IPv4 address space.
2. Private IP Address
- Definition: IP addresses reserved for use within local networks (LAN/WLAN).
- Scope: Not routable on the Internet; only valid inside the private network.
- Common ranges (IPv4):
- 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
- Use case: Home Wi‑Fi devices, office computers, printers.
- Pros: Conserves public IPs, more secure.
- Cons: Needs NAT to access the Internet.
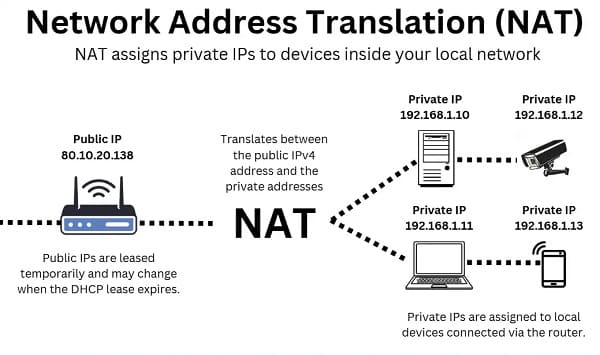
3. NAT (Network Address Translation)
- Definition: A process where a router translates private IP addresses into a public IP address for Internet communication.
- How it works:
- Your laptop (192.168.1.5) sends a request → router replaces it with the public IP (e.g., 203.0.113.25).
- The router keeps a translation table to know which private device made the request.
- Types of NAT:
- Static NAT: One private IP ↔ one public IP.
- Dynamic NAT: Private IPs mapped to a pool of public IPs.
- PAT (Port Address Translation): Many private IPs share one public IP using different port numbers (most common in home routers).
- Benefits:
- Saves IPv4 addresses.
- Adds a layer of security (internal devices aren’t directly exposed).
- Drawback: Can complicate peer‑to‑peer apps or hosting servers.
4. Putting It Together
- Private IPs are used inside your home/office LAN.
- Public IPs are used to communicate on the Internet.
- NAT bridges the two, allowing multiple private devices to share a single public IP.
Article Title:《Public vs Private IP & NAT》
Article Link:
https://sslgadgets.com/internet/networking/ip-addressing/what-is-nat/
Images and content in this article are sourced from the internet. If any copyright infringement is found, please contact us for removal.




Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up