📡 Bandwidth and Data Units Explained
1. Bandwidth
- Definition: Bandwidth is the maximum data transfer rate of a network connection.
- Unit: Measured in bits per second (bps).
- Common multiples:
- Kbps = kilobits per second (1,000 bps)
- Mbps = megabits per second (1,000,000 bps)
- Gbps = gigabits per second (1,000,000,000 bps)
- Example: A home fiber connection might be 100 Mbps, meaning it can transfer 100 million bits every second.
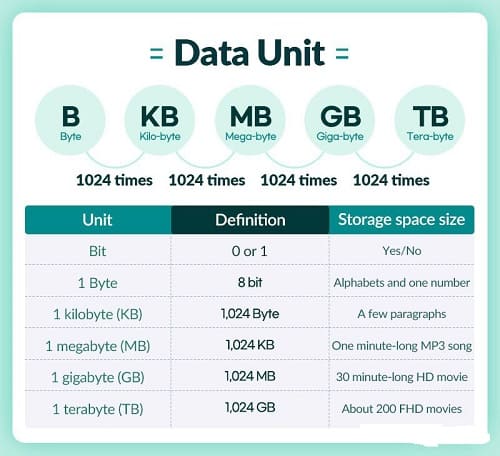
2. Data Units
- Definition: Data refers to the amount of information stored or transferred.
- Unit: Measured in bytes (B).
- 1 byte = 8 bits.
- Common multiples:
- KB = kilobyte (1,000 bytes)
- MB = megabyte (1,000,000 bytes)
- GB = gigabyte (1,000,000,000 bytes)
- TB = terabyte (1,000,000,000,000 bytes)
- Example: A movie file might be 2 GB in size.
3. Bandwidth vs Data Units
- Bandwidth = speed (how fast data moves).
- Data units = size (how much data you have).
- Relationship:
- If your bandwidth is 10 Mbps, downloading a 10 MB file takes about 8 seconds (because 10 MB = 80 Mb, and 80 ÷ 10 = 8).
4. Conversion Cheat Sheet
| Concept | Unit | Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 1 Mbps | 1,000,000 bits per second |
| Size | 1 MB | 8,000,000 bits |
| Rule of Thumb | To estimate download time: File size (MB) × 8 ÷ Bandwidth (Mbps) |
5. Examples
- Streaming video: Netflix HD requires ~5 Mbps bandwidth.
- Downloading a file: A 1 GB file on a 100 Mbps connection takes ~80 seconds.
- Cloud storage: Uploading 10 GB of photos on a 20 Mbps connection takes ~1 hour.
✅ Summary:
- Bandwidth measures speed in bits per second (bps).
- Data units measure size in bytes (B).
- Always remember: 1 byte = 8 bits.
- To calculate transfer time, convert file size into bits and divide by bandwidth.



Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up