DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
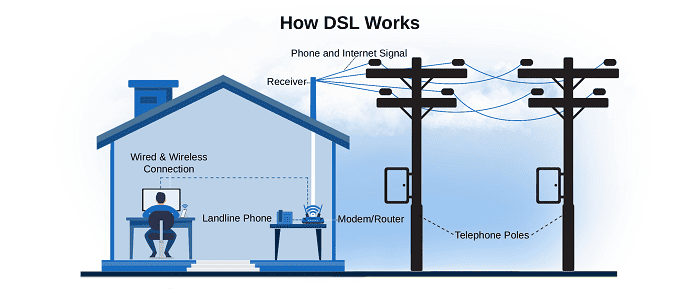
- Technology: Uses existing telephone lines (twisted copper pairs) to transmit digital data.
- Speed Range:
- Download: 1–100 Mbps (depending on distance and DSL variant: ADSL, VDSL).
- Upload: 1–10 Mbps, usually much slower than download.
- Pros:
- Widely available (uses existing phone infrastructure).
- Affordable entry-level broadband.
- Cons:
- Speed decreases with distance from the provider’s central office.
- Limited maximum bandwidth compared to newer technologies.
- Best For: Rural or suburban areas where fiber/cable is not yet deployed.
Cable Internet
- Technology: Uses coaxial cables originally designed for cable TV.
- Speed Range:
- Download: 50 Mbps – 1 Gbps (some providers offer up to 2 Gbps).
- Upload: 5–50 Mbps (often much lower than download).
- Pros:
- Faster than DSL.
- Widely available in urban and suburban areas.
- Cons:
- Shared bandwidth: speeds can drop during peak hours.
- Upload speeds are limited.
- Best For: Households needing higher speeds for streaming, gaming, and multiple devices.
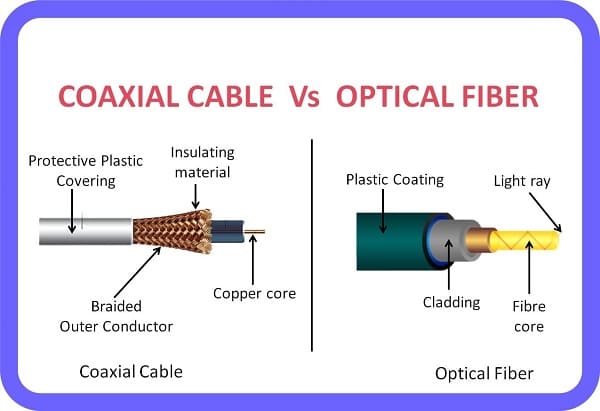
Fiber Internet
- Technology: Uses fiber-optic cables that transmit data as light signals.
- Speed Range:
- Download & Upload: 1–10 Gbps (symmetrical).
- Experimental networks can reach 100 Gbps+.
- Pros:
- Fastest speeds available.
- Symmetrical upload/download.
- Low latency, highly reliable.
- Cons:
- Expensive to build and install.
- Limited availability in rural areas.
- Best For: Heavy users, businesses, and future-proof households.
Satellite Internet
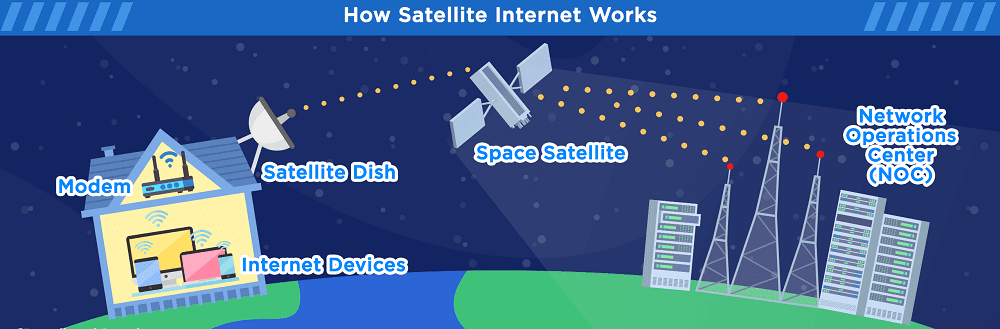
- Technology: Data transmitted via satellites orbiting Earth to ground receivers.
- Speed Range:
- Download: 25–250 Mbps (Starlink and modern providers).
- Upload: 5–20 Mbps.
- Pros:
- Available almost anywhere, even remote areas.
- Cons:
- High latency (signal travels thousands of km to space).
- Weather-sensitive.
- More expensive than DSL/Cable.
- Best For: Remote or rural areas without wired infrastructure.
Mobile Broadband (4G/5G)

- Technology: Uses cellular networks to provide internet access.
- Speed Range:
- 4G LTE: 10–100 Mbps.
- 5G: 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps+ (under ideal conditions).
- Pros:
- Portable, works anywhere with cell coverage.
- Easy to set up (no cables).
- Cons:
- Dependent on signal strength and coverage.
- Data caps may apply.
- Best For: On-the-go users, backup internet, or areas with strong mobile coverage.
| Type | Technology | Speed Range | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSL | Telephone lines | 1–100 Mbps / 1–10 Mbps | Widely available, cheap | Slow, distance-sensitive | Rural/suburban |
| Cable | Coaxial cables | 50 Mbps–1 Gbps / 5–50 Mbps | Faster than DSL, common | Shared bandwidth, weak upload | Urban households |
| Fiber | Fiber-optic cables | 1–10 Gbps+ (symmetrical) | Fastest, reliable, low latency | Expensive, limited coverage | Heavy users/business |
| Satellite | Satellites | 25–250 Mbps / 5–20 Mbps | Works anywhere | High latency, weather issues | Remote areas |
| Mobile | Cellular (4G/5G) | 10 Mbps–1 Gbps+ | Portable, flexible | Coverage/data caps | On-the-go users |
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)

Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up