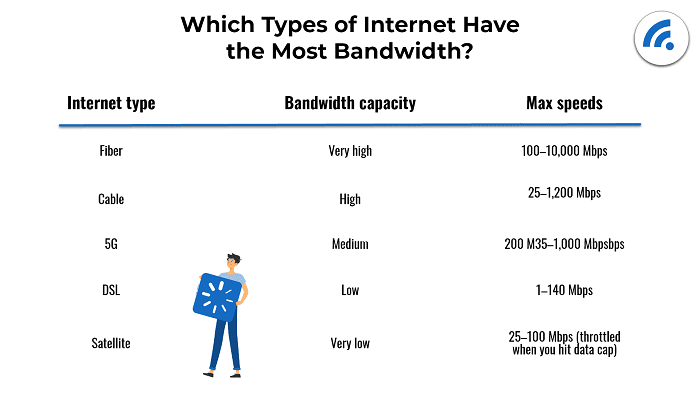
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given time. Usually measured in bits per second (bps), such as Mbps (megabits per second) or Gbps (gigabits per second).
Key Points
- Capacity, not speed: Bandwidth is about how much data can move, not how fast a single bit travels.
- Shared resource: In shared networks, multiple users divide the available bandwidth.
- Different from throughput:
- Bandwidth = theoretical maximum capacity.
- Throughput = actual data transfer rate achieved in practice.
Speed
Speed in networking refers to how quickly data travels from one point to another. It is the rate of data transfer experienced by the user, often measured in bits per second (bps), just like bandwidth.
Key Points
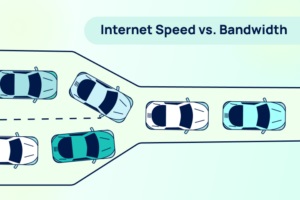
- User experience: Speed is what you notice when browsing, streaming, or downloading.
- Different from bandwidth:
- Bandwidth = maximum capacity (how many lanes).
- Speed = how fast data flows (car velocity).
- Influenced by many factors:
- Bandwidth limit from ISP
- Network congestion
- Latency (delay)
- Router/Wi‑Fi quality
- Device performance
Bandwidth vs Speed vs Throughput
| Term | Definition | Example | Key Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Maximum capacity of a network link, measured in bits per second (bps). | A fiber line with 1 Gbps bandwidth | Think of it as the width of the highway (how many cars can fit). |
| Speed | How fast a single bit travels through the medium (signal propagation). | Light travels in fiber at ~200,000 km/s | It’s about latency or how quickly one car moves. |
| Throughput | Actual amount of data successfully transmitted per second in practice. | A 1 Gbps link but only 600 Mbps achieved due to congestion | It’s the real traffic flow on the highway. |
Is Bandwidth the Same as “Fastest Speed”?
Bandwidth ≠ Speed
- Bandwidth = the capacity of a network link (how much data can be carried per second).
- Speed = the rate you experience when data actually moves (how quickly a file downloads or a video streams).
- Bandwidth is like the width of a highway (how many lanes).
- Speed is like the velocity of cars on that highway.
Why People Confuse Them
- Internet providers often advertise “high bandwidth” as “fast internet.”
- In practice, higher bandwidth can allow faster downloads, but only if other conditions (congestion, latency, device limits) don’t slow things down.
Relationship Between Bandwidth and Speed
- Bandwidth sets the upper limit of possible speed.
- Speed depends on bandwidth plus other factors:
- Network congestion (too many cars on the highway)
- Latency (delays in transmission)
- Device/router performance
- Wi‑Fi interference or distance
- Throughput = the actual speed achieved in practice (often lower than bandwidth).
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)

Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up