What is a Data Unit?
A data unit is the basic piece of information used in computing and networking. Depending on the context, it can mean:
- Storage units → how much data is stored (KB, MB, GB, etc.)
- Transmission units → how data is structured when sent across a network (bit, frame, packet, etc.)
Storage / Capacity Data Units
These measure the size of data in computers and digital systems:
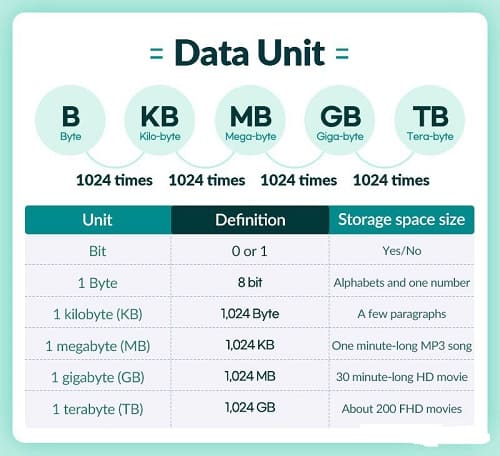
- Bit (b) → smallest unit, 0 or 1
- Byte (B) → 8 bits
- Kilobyte (KB) → ≈ 1,000 bytes (sometimes 1,024 in computing)
- Megabyte (MB) → ≈ 1,000 KB
- Gigabyte (GB) → ≈ 1,000 MB
- Terabyte (TB) → ≈ 1,000 GB
- Petabyte (PB) → ≈ 1,000 TB
Used to describe file sizes, disk capacity, memory, and bandwidth.
Networking Transmission Data Units (OSI Model)
These describe how data is packaged and transmitted across networks:
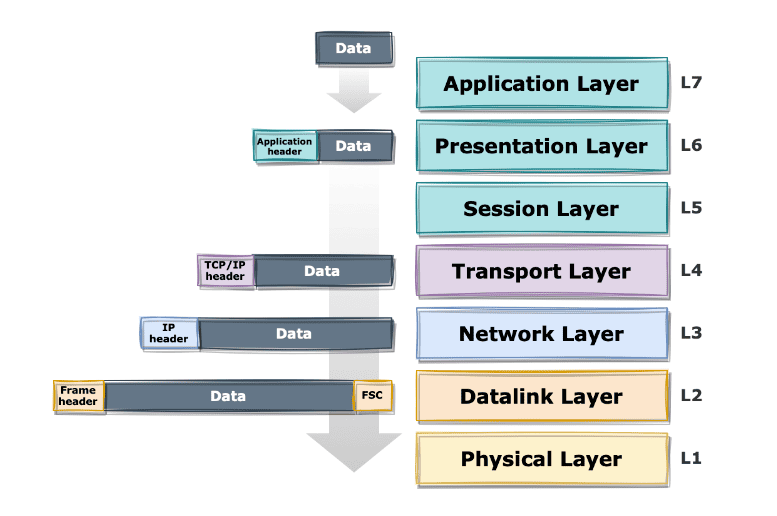
- Bit → Physical layer (raw 0s and 1s as signals)
- Frame → Data Link layer (MAC addresses, error detection)
- Packet → Network layer (IP addresses, routing info)
- Segment (TCP) / Datagram (UDP) → Transport layer (port numbers, sequencing, reliability)
- Message → Application layer (actual user data, e.g. email, web request)
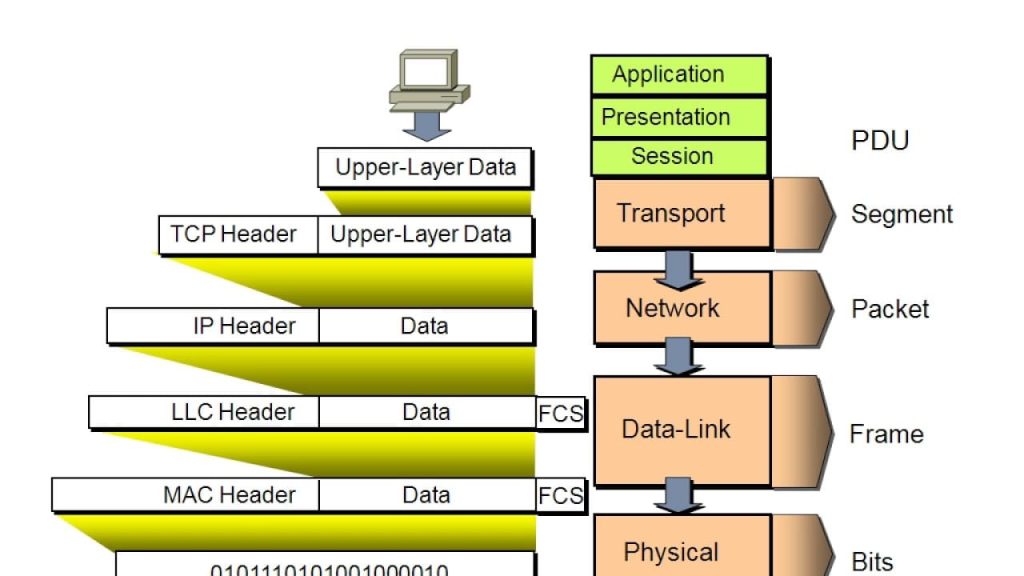
Each layer adds headers/trailers to guide transmission and ensure reliable communication.
Bandwidth and Data Units
- Bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps), e.g. 100 Mbps or 1 Gbps.
- It tells you how much data can be transmitted per second.
- Here, the storage units (bits, bytes, KB, MB) connect directly to networking performance.
Final Summary
- Storage Data Units → KB, MB, GB, TB (measure data size).
- Networking Data Units → Bit, Frame, Packet, Segment, Message (structure for transmission).
- Bandwidth → measured in bits per second, showing how fast data units move across a network.
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)

Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up