WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
A WLAN is a type of LAN (Local Area Network) that uses wireless communication (radio waves) instead of physical cables to connect devices. The most common WLAN technology is Wi‑Fi (IEEE 802.11 standard).
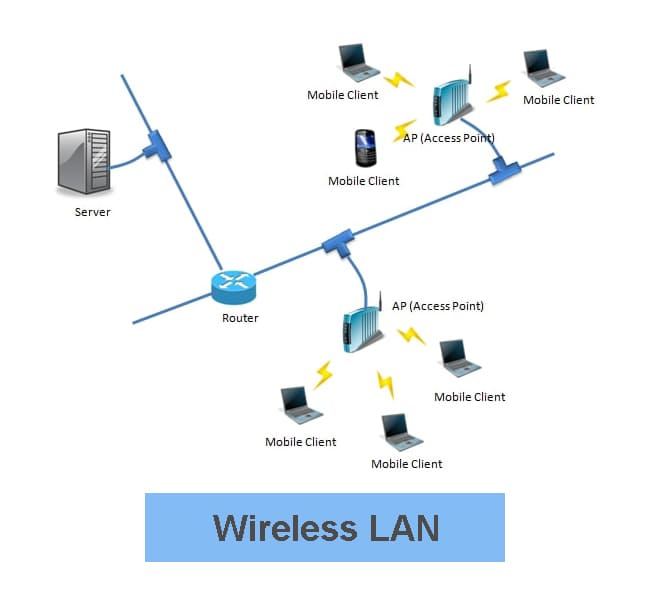
Key Characteristics
- Coverage: Limited to a local area (home, office, campus).
- Medium: Uses radio waves instead of Ethernet cables.
- Access Point: Devices connect through a wireless router or access point.
- Mobility: Users can move freely within the coverage area while staying connected.
- Speed: Depends on Wi‑Fi standard (e.g., Wi‑Fi 5, Wi‑Fi 6, Wi‑Fi 7).
Wi‑Fi: Standards, Versions, and History
1. Origins
- 1997: First Wi‑Fi standard (IEEE 802.11) introduced, max speed only 2 Mbps.
- Developed by the IEEE Standards Association, Wi‑Fi quickly became the dominant wireless LAN technology worldwide.
2. Generations of Wi‑Fi
| Generation | Standard | Year | Band | Max Speed | Key Features |
| Wi‑Fi 1 | 802.11 | 1997 | 2.4 GHz | 2 Mbps | First Wi‑Fi standard |
| Wi‑Fi 2 | 802.11b | 1999 | 2.4 GHz | 11 Mbps | Affordable, but interference-prone |
| Wi‑Fi 3 | 802.11g | 2003 | 2.4 GHz | 54 Mbps | Faster, backward compatible |
| Wi‑Fi 4 | 802.11n | 2009 | 2.4 & 5 GHz | 600 Mbps | Introduced MIMO, dual-band |
| Wi‑Fi 5 | 802.11ac | 2014 | 5 GHz | 1.3 Gbps | Beamforming, better streaming |
| Wi‑Fi 6 | 802.11ax | 2019 | 2.4 & 5 GHz | 9.6 Gbps | OFDMA, improved efficiency |
| Wi‑Fi 6E | 802.11ax (extended) | 2021 | 6 GHz | 9.6 Gbps | New 6 GHz band, less congestion |
| Wi‑Fi 7 | 802.11be | 2024 | 2.4/5/6 GHz | ~46 Gbps | Multi-link operation, ultra-low latency |
Evolution Highlights
- Early Wi‑Fi (1997–2003): Slow speeds, mainly for basic web browsing.
- Wi‑Fi 4 (2009): Big leap with MIMO (multiple antennas) and dual-band support.
- Wi‑Fi 5 (2014): Optimized for HD video streaming and gaming.
- Wi‑Fi 6/6E (2019–2021): Focused on efficiency, handling many devices simultaneously.
- Wi‑Fi 7 (2024): Designed for ultra-fast speeds, AR/VR, and next-gen cloud applications.
4. Why It Matters
- Speed: From 2 Mbps (Wi‑Fi 1) to ~46 Gbps (Wi‑Fi 7).
- Frequency bands: Expanded from 2.4 GHz → 5 GHz → 6 GHz.
- Applications: From simple browsing → HD streaming → IoT → AR/VR.
WLAN vs LAN
| Feature | LAN (general) | WLAN (wireless LAN) |
| Connection | Wired (Ethernet cables) | Wireless (Wi‑Fi radio waves) |
| Mobility | Limited (fixed cables) | High (move freely with devices) |
| Speed | Very stable, up to 10 Gbps | Variable, depends on Wi‑Fi standard |
| Setup | Requires cabling | Easier, just router + Wi‑Fi |
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)

Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up