A router is a device that sits at the boundary between networks and decides where to send data packets. It connects multiple IP networks or subnetworks and ensures that traffic flows efficiently.
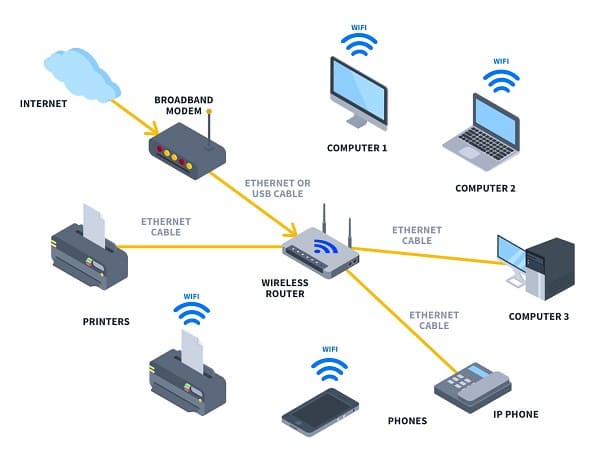
Core Functions
- Traffic management: Examines packet destination IP addresses and forwards them to the right network.
- Routing table: Maintains a list of possible paths and chooses the most efficient one.
- NAT (Network Address Translation): Allows multiple devices in a LAN to share one public IP.
- Firewall/security: Many routers block unauthorized traffic.
- DHCP: Often assigns IP addresses to devices automatically.
Types of Routers
- Home/Small office routers: Combine routing, Wi‑Fi, firewall, and DHCP in one device.
- Enterprise routers: Handle large volumes of traffic, often with advanced routing protocols.
- Core/Edge routers: Used by ISPs to manage Internet backbone traffic.
Router vs Switch vs Modem
| Device | Role | Layer | Example |
| Router | Connects different networks, directs packets | Layer 3 (Network) | Home router linking LAN to Internet |
| Switch | Connects devices within one LAN | Layer 2 (Data Link) | Office switch connecting PCs & printers |
| Modem | Converts signals for ISP connection | Layer 1 (Physical) | DSL/cable modem providing Internet |
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)

Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up