Traditional Meaning
A modem (short for modulator–demodulator) is a device that converts signals so your computer or router can communicate with your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Modem = Modulator–Demodulator.
- Originally used in dial‑up Internet (1980s–1990s), converting digital signals ↔ analog telephone signals.
- Later expanded to DSL modems (telephone lines) and Cable modems (TV coaxial lines).
- In all cases, the modem’s role was to translate signals between your local network and the ISP.

Fiber Era: ONT
- With fiber‑optic Internet (FTTH, Fiber to the Home), the device provided by the ISP is called an ONT (Optical Network Terminal).
- ONT’s role:
- Converts light signals from fiber into electrical Ethernet signals.
- Provides a port for your router or computer.
- Technically, the ONT is not a “modem” in the old sense, but it performs the same essential function: translating ISP signals into usable digital form.
Core Functions
- Modulation: Converts digital data into analog or carrier signals for transmission.
- Demodulation: Converts received signals back into digital data.
- Physical link: Provides the actual connection between your home/office network and the ISP.
Types of Modems
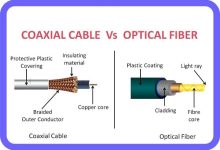
- DSL Modem: Uses telephone lines (Digital Subscriber Line).
- Cable Modem: Uses coaxial cable TV lines.
- Fiber Modem (ONT): Optical Network Terminal for fiber connections.
- Dial‑up Modem: Legacy technology using analog phone lines (very slow).
- Cellular Modem: Uses mobile networks (3G/4G/5G) for Internet access.
Modem vs Router vs Switch
| Device | Role | OSI Layer | Example |
| Modem | Converts signals, connects to ISP | Layer 1 (Physical) | DSL/cable/fiber modem |
| Router | Connects different networks, directs packets | Layer 3 (Network) | Home router linking LAN to Internet |
| Switch | Connects devices within LAN, forwards by MAC | Layer 2 (Data Link) | Office switch connecting PCs & printers |
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)

Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up