Static IP
- Definition: An IP address that is manually assigned to a device and does not change.
- Characteristics:
- Permanent, fixed address.
- Often used for servers, printers, or devices that must always be reachable at the same IP.
- Pros: Reliable for hosting websites, remote access, or networked devices.
- Cons: Requires manual setup, less flexible, can expose devices to security risks if not managed properly.
Dynamic IP
- Definition: An IP address that is automatically assigned by a DHCP server and may change over time.
- Characteristics:
- Temporary, changes when devices reconnect or after a lease expires.
- Commonly used for home users and mobile devices.
- Pros: Easier to manage, conserves IP addresses, more secure (harder to target).
- Cons: Not suitable for servers or services that need a consistent address.
Putting It Together
- Static IP: Fixed, set manually. Best for servers.
- Dynamic IP: Assigned automatically, changes over time. Best for everyday devices.
Example
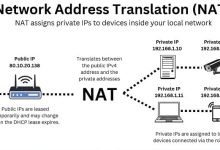
- Home Wi‑Fi: Your router uses DHCP to give your phone a dynamic IP (e.g., 192.168.1.12).
- Office printer: IT sets a static IP (e.g., 192.168.1.50) so everyone can always find it.
- Web server: Needs a static public IP (e.g., 203.0.113.25) so clients can connect reliably.
Summary:
- Static IP = fixed, manual, reliable for servers.
- Dynamic IP = automatic, flexible, common for users.
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)



Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up