🏢 What Is a Data Center?
- Definition: A data center is a physical facility that organizations use to house computer systems and associated components, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment.
- Purpose: Provides centralized resources for storing, processing, and distributing data.
- Role in Infrastructure: Acts as the backbone for cloud computing, enterprise IT, and global internet services.
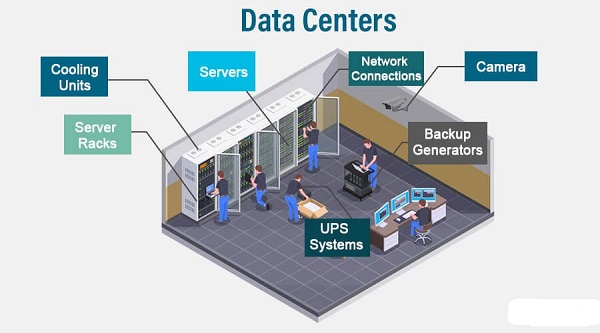
⚙️ Key Components
- Servers → Run applications, websites, and services.
- Storage Systems → Hold massive amounts of data (databases, files, backups).
- Networking Equipment → Switches, routers, firewalls to connect internally and externally.
- Power Supply → Redundant electricity sources, UPS (uninterruptible power supply), backup generators.
- Cooling Systems → Air conditioning, liquid cooling to prevent overheating.
- Security → Physical (guards, biometrics) and digital (firewalls, intrusion detection).
🧩 Types of Data Centers
- Enterprise Data Centers → Owned and operated by a single company for internal use.
- Colocation Data Centers → Rent space, power, and cooling to multiple customers.
- Cloud Data Centers → Operated by providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud.
- Edge Data Centers → Smaller facilities located closer to users/devices to reduce latency.
🌍 Global Scale
- Thousands of data centers worldwide.
- Hyperscale data centers (like those of Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Meta) host millions of servers.
- Located strategically near power sources, fiber‑optic hubs, and major population centers.
📌 Why They Matter
- Enable cloud services, streaming, social media, e‑commerce, and enterprise IT.
- Provide redundancy and disaster recovery.
- Support global connectivity alongside submarine cables and IP/DNS infrastructure.
📌 Summary Sentence
“A data center is a secure facility housing server, storage, and networking systems, forming the backbone of cloud computing and global internet services.”






Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up