🌐 IP Address Allocation
1. Definition
IP address allocation is the hierarchical infrastructure process of distributing unique numerical identifiers (IP addresses) to networks and devices, ensuring that data can be correctly routed across the global internet.
2. IP Address Space
- IPv4:
- 32‑bit address space.
- Total: about 4.3 billion unique addresses.
- Nearly exhausted due to early uneven distribution and explosive internet growth.
- IPv6:
- 128‑bit address space.
- Total: about 3.4 × 10^38 addresses (virtually unlimited).
- Designed to replace IPv4 and support future scalability.
3. Global Governance
- IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority):
- Operates under ICANN.
- Manages the global pool of IP addresses.
- Allocates large address blocks to Regional Internet Registries (RIRs).
- Regional Internet Registries (RIRs):
- Each RIR manages IP distribution in its region:
- ARIN → North America
- RIPE NCC → Europe, Middle East, Central Asia
- APNIC → Asia-Pacific
- LACNIC → Latin America, Caribbean
- AFRINIC → Africa
- Each RIR manages IP distribution in its region:
- ISPs / Telecom Providers / Large Organizations:
- Receive allocations from RIRs.
- Use them to build infrastructure and provide connectivity.
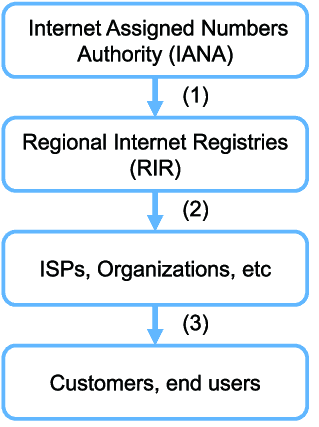
4. Allocation Hierarchy
IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)
- Manages the global pool of IP addresses.
- Allocates large blocks to Regional Internet Registries (RIRs).
RIRs (Regional Internet Registries)
- Distribute IP address blocks within their regions:
- ARIN → North America
- RIPE NCC → Europe, Middle East, Central Asia
- APNIC → Asia-Pacific
- LACNIC → Latin America, Caribbean
- AFRINIC → Africa
ISPs / Telecom Providers / Enterprises
- Receive allocations from RIRs.
- Use them to build infrastructure and provide connectivity.
End Networks / Users
- Ultimately get IP addresses through ISPs or organizational networks.
This hierarchy ensures global uniqueness and efficient routing.
5. Who Gets the IPs?
- Large organizations & governments → sometimes receive blocks directly from RIRs.
- ISPs & telecom providers → get large allocations to serve millions of customers.
- Data centers & cloud providers → need massive address pools for servers and virtual machines.
- Ordinary users & devices → receive addresses indirectly via ISPs.
6. Why It’s Infrastructure
- IP allocation is part of the internet backbone, alongside DNS, routing protocols (BGP), and physical cabling.
- Without it, devices cannot be uniquely identified or communicate.
- It underpins higher-level services like websites, apps, and cloud platforms.
🌐 Public IP Addresses
- Definition: Unique addresses that are globally routable on the internet.
- Purpose: Identify devices/networks directly accessible from anywhere online.
- Allocation: Assigned by ISPs from blocks they receive from RIRs.
- Example:
8.8.8.8(Google DNS).
🏠 Private IP Addresses
- Definition: IP ranges reserved for use inside local/private networks, not routable on the public internet.
- Purpose: Allow devices in homes, offices, or enterprises to communicate internally.
- Ranges (IPv4):
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
- Example:
192.168.1.1(common home router address).
📌 Reserved IP Addresses
- Definition: Special blocks set aside for specific uses, not for general public allocation.
- Examples:
- Loopback:
127.0.0.0/8→ refers to the local machine (127.0.0.1). - Link-local:
169.254.0.0/16→ auto-assigned when DHCP fails. - Multicast:
224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255. - Broadcast:
255.255.255.255. - Documentation/Test:
192.0.2.0/24,198.51.100.0/24,203.0.113.0/24.
- Loopback:
📊 Summary Table
| Category | Routable on Internet | Example Range / Address | Purpose | Quantity (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public IP | Yes | 8.8.8.8 | Global communication | ~3.7 billion usable (out of 4.3 billion total IPv4) |
| Private IP | No | 192.168.0.0/16 | Local networks (home/office) | ~18 million addresses across 3 reserved ranges |
| Reserved IP | No (special use) | 127.0.0.1, 169.254.0.0/16 | Loopback, link-local, multicast | ~600 million+ reserved for special functions |
📌 Summary Sentence
“IPv4 has about 4.3 billion addresses (mostly exhausted), while IPv6 has ~3.4×10^38. IANA allocates blocks to RIRs, which distribute them to ISPs, telecoms, enterprises, and cloud providers, who then assign them to end networks and devices.”





Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up