How Satellite Links Work
- Uplink: Ground station sends a signal to the satellite.
- Satellite Relay: Satellite receives, amplifies, and retransmits the signal.
- Downlink: Signal is sent back to another ground station or directly to user equipment (like a satellite dish).
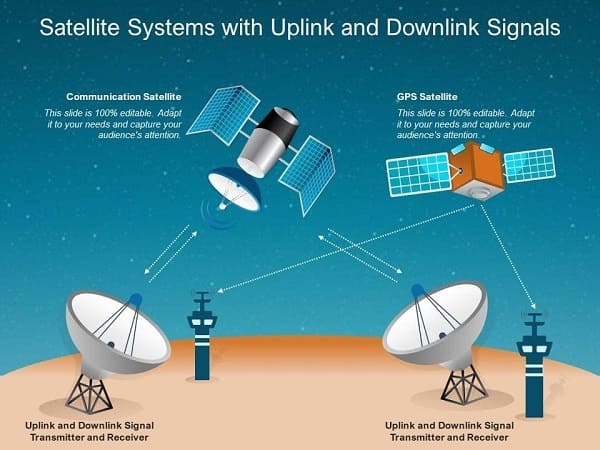
Types of Satellite Links
- Geostationary (GEO):
- Orbit ~35,786 km above Earth.
- Fixed position relative to Earth.
- High coverage, but higher latency (~600 ms round trip).
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO):
- Orbit ~2,000–20,000 km.
- Lower latency than GEO.
- Used for navigation systems (e.g., GPS, Galileo).
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO):
- Orbit ~500–2,000 km.
- Very low latency (~20–40 ms).
- Requires large constellations (e.g., Starlink, OneWeb).
Applications
- Global Internet Access: Starlink, OneWeb, Amazon Kuiper.
- Telecommunications: Voice/data in remote areas, ships, aircraft.
- Broadcasting: TV, radio, live events.
- Navigation: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou.
- Military & Disaster Recovery: Secure communications where infrastructure is damaged or unavailable.
Comparison with Other Infrastructure
| Feature | Submarine Cables | Terrestrial Fiber | Satellite Links |
| Coverage | Intercontinental | National/regional | Global, including remote areas |
| Latency | Very low | Very low | Higher (depends on orbit) |
| Capacity | Extremely high | Extremely high | Lower than fiber/cables |
| Reliability | High | High | Weather/space conditions affect |
| Deployment | Undersea cable ships | Underground/land routes | Launch satellites into orbit |
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)




Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up