🎤 1. What Is a Microphone?
A microphone is a transducer that converts sound waves (acoustic energy) into electrical signals. In computers, microphones capture voice or audio for communication, recording, streaming, and voice recognition. The microphone was first created by Emile Berliner in 1877 as a carbon button microphone.
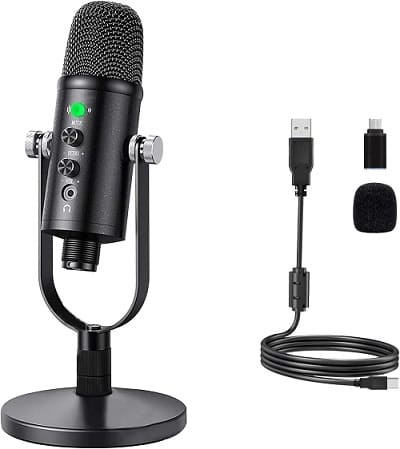

🧩 2. Types of Microphones
| Type | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Microphone | Uses a moving coil; durable, handles loud sounds | Live performances, broadcasting |
| Condenser Microphone | Uses a charged diaphragm; sensitive, wide frequency response | Studio recording, streaming |
| Ribbon Microphone | Uses a thin ribbon; warm sound, fragile | Vintage recording, specialized studios |
| Electret Condenser | Miniaturized condenser mic; low cost | Built-in laptop/phone mics |
| USB Microphone | Plug-and-play digital mic | Podcasting, online meetings |
| Wireless Microphone | Transmits audio via RF/Bluetooth | Stage, presentations |
| Lavalier (Clip-on) | Small, wearable mic | Interviews, presentations |
| Shotgun Microphone | Highly directional | Film, video production |
⚙️ 3. Key Specifications
- Frequency Response: Range of sound captured (e.g., 20 Hz – 20 kHz).
- Polar Pattern: Directionality of sound pickup:
- Cardioid: Front-focused (common for vocals)
- Omnidirectional: All directions
- Bidirectional: Front and back (figure-8)
- Shotgun: Narrow, highly directional
- Sensitivity: How well it picks up quiet sounds.
- Impedance: Electrical resistance; affects compatibility.
- Connectivity: Analog (XLR, 3.5mm) vs digital (USB, Lightning).
🕰️ 4. Brief History
- 1877: First microphone invented by Emile Berliner (carbon button mic).
- 1920s–1930s: Dynamic and condenser microphones developed.
- 1950s–1970s: Ribbon microphones popular in broadcasting.
- 1990s–2000s: Miniaturized electret condensers integrated into laptops and phones.
- 2010s–2020s: USB and wireless microphones dominate podcasting, streaming, and conferencing.






Must log in before commenting!
Sign Up