A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in a computer. It connects and allows communication between the CPU, RAM, storage, GPU, power supply, and peripheral devices. It also houses the chipset, which controls data flow between components.
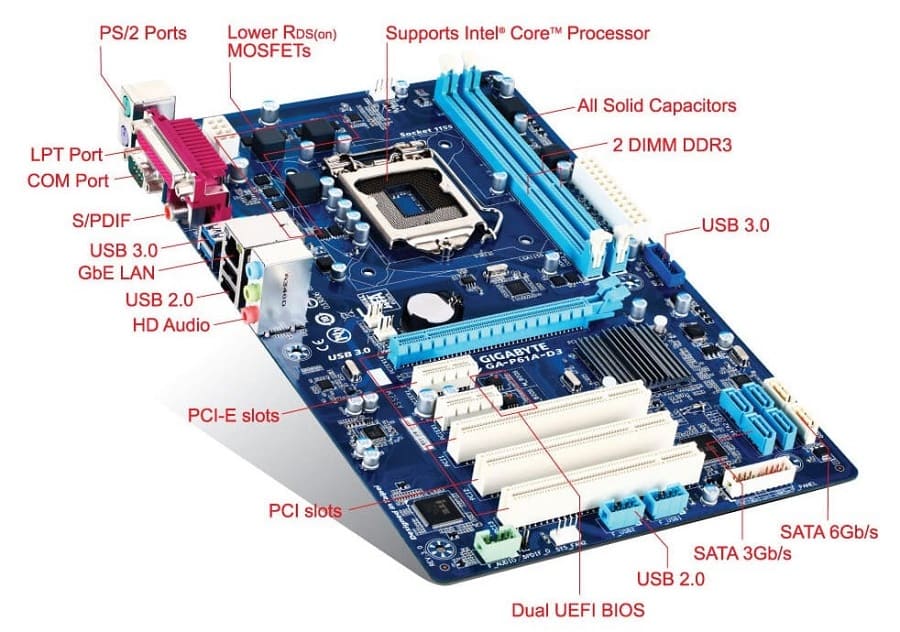
Key Components on a Motherboard
| Component | Function |
| CPU Socket | Holds the processor (e.g., LGA1700 for Intel, AM5 for AMD) |
| RAM Slots (DIMM) | Install system memory (DDR3/4/5) |
| Chipset (PCH) | Manages communication between CPU, RAM, storage, USB, etc. |
| Power Connectors | ATX 24-pin (main), 8-pin (CPU), others for GPU |
| PCIe Slots | For GPUs, SSDs, sound/network cards |
| M.2 / SATA Ports | For SSDs and HDDs |
| BIOS/UEFI Chip | Firmware that initializes hardware and loads the OS |
| VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) | Regulate power to CPU and memory |
| I/O Ports | USB, HDMI, Ethernet, audio, etc. on the rear panel |
| Fan Headers / RGB Headers | For cooling and lighting control |
Motherboard Form Factors
| Form Factor | Size | Use Case |
| ATX | 305 × 244 mm | Full-size desktops, gaming rigs |
| Micro-ATX | 244 × 244 mm | Budget/mid-range desktops |
| Mini-ITX | 170 × 170 mm | Compact PCs, HTPCs |
| E-ATX | 305 × 330 mm | High-end workstations, multi-GPU setups |
Chipsets and Platform Support
- Intel Chipsets: Z790, B760, H610 (12th–14th Gen Core CPUs)
- AMD Chipsets: X670, B650, A620 (Ryzen 7000 series, AM5 socket)
- Chipset determines:
- PCIe lane count and version (e.g., PCIe 4.0 vs 5.0)
- USB/Thunderbolt support
- Overclocking support (Z-series for Intel, X-series for AMD)
- RAID, Wi-Fi, and storage features
Laptop vs Desktop Motherboard Comparison
| Feature | Laptop Motherboard | Desktop Motherboard |
| Size & Form Factor | Compact, custom-shaped for chassis | Standardized (ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX) |
| CPU Socket | Often soldered (BGA); non-upgradable | Uses replaceable socket (e.g., LGA, AM5) |
| RAM Slots | Limited (1–2 SO-DIMM slots); sometimes soldered | 2–4 DIMM slots; easily upgradeable |
| GPU Support | Integrated GPU or soldered discrete GPU | Dedicated PCIe slot for GPU upgrades |
| Storage Interface | M.2 NVMe, SATA (limited space) | Multiple M.2, SATA ports; more flexibility |
| Expansion Slots | Rare or none | PCIe slots for GPU, sound, network cards |
| Cooling System | Compact heat pipes and fans | Larger heatsinks, fans, liquid cooling options |
| Power Supply | Uses external adapter; onboard power regulation | ATX power supply with 24-pin and 8-pin connectors |
| BIOS/UEFI Access | Limited options; locked features | Full access; supports overclocking and tuning |
| Repairability | Low; components often soldered | High; modular and replaceable parts |
| Customization | Minimal; designed for portability | High; supports custom builds and upgrades |
| Use Case | Portable computing, energy-efficient | High performance, gaming, workstation tasks |
How the Motherboard Connects Everything
- CPU ↔ RAM: via memory controller (on CPU)
- CPU ↔ GPU: via PCIe x16 slot
- CPU ↔ Chipset: via DMI (Intel) or Infinity Fabric (AMD)
- Chipset ↔ Storage/USB/Audio: handles I/O and peripheral traffic
- BIOS/UEFI: initializes all components and hands off to the OS
Choosing a Motherboard — What to Consider
- CPU compatibility (socket + chipset)
- RAM support (DDR4 vs DDR5, max capacity, speed)
- Expansion needs (PCIe slots, M.2 slots, USB ports)
- Form factor (case size and airflow)
- Power delivery (VRM quality for overclocking)
- Connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, Thunderbolt)
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)





Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up