A cooling system in a computer manages heat generated by components like the CPU, GPU, VRMs, and storage. Without proper cooling, these parts can throttle performance, crash, or suffer permanent damage.
Types of Cooling Systems
| Type | Description | Use Case |
| Air Cooling | Uses heatsinks and fans to dissipate heat | Most desktops and laptops |
| Liquid Cooling (AIO/Custom Loop) | Circulates coolant through a loop to transfer heat to a radiator | High-performance PCs, overclocking |
| Passive Cooling | No fans; relies on heat sinks and airflow | Silent systems, embedded devices |
| Vapor Chamber | Flat heat spreader using phase-change cooling | High-end GPUs, gaming laptops |
| Thermoelectric (Peltier) | Uses electric current to move heat | Experimental or niche cooling |
| Immersion Cooling | Hardware submerged in non-conductive fluid | Data centers, extreme HPC setups |
Key Components in a Cooling System
- Heatsink: Metal block (usually aluminum or copper) that absorbs and spreads heat
- Fan: Moves air across heatsinks or through the case
- Thermal Paste: Fills microscopic gaps between CPU/GPU and heatsink for better heat transfer
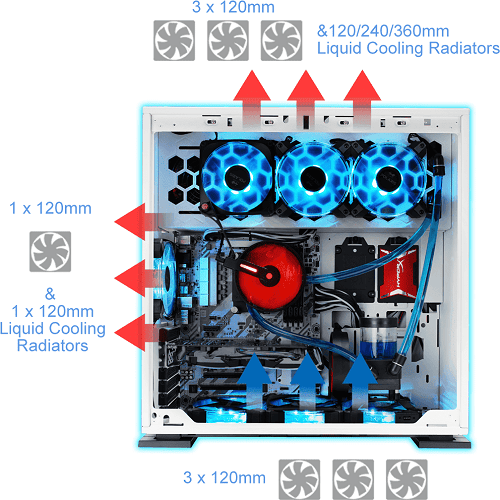
- Radiator: In liquid cooling, dissipates heat from coolant
- Pump: Circulates coolant in liquid systems
- Coolant: Liquid medium (water or special fluid) in liquid cooling
- Sensors: Monitor temperature and control fan speeds
-=||=-FavoriteLike (0)





Must log in before commenting!
Sign In Sign Up