Public IP vs Private IP & NAT
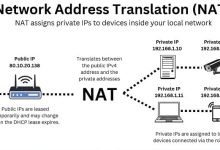
Public IP Address Private IP Address NAT (Network Address Translation) Putting It Together

Public IP Address Private IP Address NAT (Network Address Translation) Putting It Together

IP Address MAC Address IP–MAC Binding Example Benefits Summary
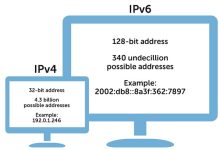
IP address allocation is the hierarchical infrastructure process of distributing unique numerical identifiers (IP addresses) to networks and devices, ensuring that data can be correctly routed across the global internet. IP Address Space Global Governance Who Gets the IPs Public IP Addresses Private IP Addresses Reserved IP Addresses Summary Table Category Routable on Internet Example Range / Address Purpose Quantity (approx.) Public IP Yes 8.8.8.8 Global communication ~3.7 billion usable (out of 4.3 billion total IPv4) Private IP No 192.168.0.0/16 Local networks (home/office) ~18 million addresses across 3 reserved ranges Reserved IP No (special use) 127.0.0.1, 169.254.0.0/16 Loopback, link-local, multicast ~600 million+ reserved for special functions “IPv4 has about 4.3 billion addresses (mostly exhausted), while IPv6 has ~3.4×10^38. IANA allocates blocks to RIRs,...

What Is a Service Provider? Internet Service Provider (ISP) Telecom Service Provider ⚙️ How They Work
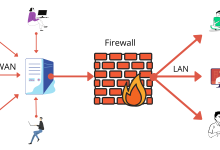
What Is a Firewall? Types of Firewalls How Firewalls Work

A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts all your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, while a Proxy simply acts as an intermediary server that hides your IP address but does not encrypt your data. VPNs provide stronger privacy and security, whereas proxies are lighter and mainly used for location spoofing or bypassing restrictions. Proxy Server VPN vs Proxy Comparison Feature VPN Proxy Encryption Yes, full traffic encrypted No encryption IP Masking Yes Yes Scope Entire device traffic Specific apps/websites only Security High (protects against hackers/ISP) Low (traffic visible to ISP/hackers) Speed Slightly slower (due to encryption) Faster, but less secure Cost Usually paid Often free or cheaper

What Is a Computer Virus? Malware Common Types of Malwares Virus Common Types of Viruses What Is Antivirus? Types of Threats Antivirus Protects Against How Antivirus Works Relationship Between Virus and Antivirus
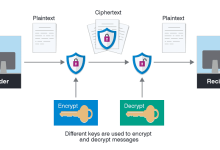
What Is Encryption Types of Encryptions Password Encryption (Process) When we talk about passwords, encryption or hashing is critical for security. Here’s the step‑by‑step process: Where Encryption Is Used Benefits

Programming (the activity) Programming is the process of designing instructions for a computer. Those instructions ultimately need to be executed by hardware (CPU, memory, I/O devices). Programmers think in algorithms, but the computer only understands electrical signals and binary (0s and 1s). Language (the tool) Programming languages are the tools that translate human logic into something hardware can execute. High‑level languages (Python, Java, PHP) are abstract and easy for humans. Low‑level languages (Assembly, C) are closer to hardware, giving more control. Compilers and interpreters act as bridges: Interpreter → translates line by line while running. Compiler → translates code into machine instructions before running. Classification Hardware How programs run Popular languages at a glance Programming + Language + Hardware Together Flow:

Mobile App A mobile app (short for mobile application) is a software program designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables. Key Points Mobile App Development Mobile app development is the process of designing, building, and deploying applications for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. These apps can be native (iOS/Android), cross‑platform, hybrid, or progressive web apps (PWAs), depending on the chosen technology stack. Platforms Languages Development Tools

Website Web Application Web Development Web development is the process of building and maintaining websites and web apps. It has two main layers: Front‑End Development (Client Side) Back‑End Development (Server Side) Full‑Stack Development Website vs. Web App “A website is an online collection of pages for presenting information, while a web application is interactive software running in the browser; web development is the structured process of building both, across front‑end and back‑end layers.”

Desktop Application Desktop App Development Approaches Core Components Development Process Tools & Languages